LabView con Ethernet IP (Industrial Protocol)
Buenos Días, una pregunta:
Connect some remotas working electrovalvulas quiero con Ethernet IP (Ethernet industrial Protocol), ¿LabView can trabajar con este protocolo?.
Tags: NI Software
Similar Questions
-
With the help of hilscher gateway for profibus to labview via ethernet
I'm not familiar with Hilscher Profibus gateways, but I'm sure that they provide an OPC server that can be accessed through functions LabVIEW DataSocket or much better performance through LabVIEW DSC. There is also a chance that Hilscher provides a DLL or same screws LabVIEW database API, but you should check with Hilscher.
From my own experience I recommend to use a gateway Comsoft FNL . Comsoft is very experienced with LabVIEW and they provide a fast and reliable VI-interface for all their interfaces Profibus.
I don't want to bash products Hilscher, but as I have no experience with their products (unlike the Comsoft products), I can't give a competent answer on their API.Best regards
Jochen Klier
National Instruments -
Protocol settings NODES in LabVIEW using NI USB-8473
Hi, I was recently introduced to this Protocol for diagnostics on the ECU.
What I want to do: -.
I want to read messages from the ECU using the program called 'UDS Diagnostic Demo', which is available in the game for example provided under the help section in LabVIEW.
I know: -.
I can communicate with ECU very well with the screws of NI-CAN and the same material (8473 NIUSB) I used initially for monitoring CAN messages.
What I want to know: -.
- I don't know about the parameters I put the Protocol Settings section if I use UDS Protocol?
- What are Transmit and receive IDs, are these specific ECU or a few standard values?
- For UDS and ISO TP Normal mode chosen - I learned I didn't need to worry about the ID of the channel and Transmit / receive address Extensions but don't I care about periodical CAN ID?
Also by reading this forum I came across an issue where it was mentioned as a transmit and receive ID 7E8 and 7E0 respectively. I also tried but no luck.
Using values as specified in the screenshot, I'm able to run the VI and it doesn't give any errors but he don't give me any respinses ECU is.
Any help will be much appreciated.
Thank you
Vicky
Hi Frank,.
I'm back with the solution. I managed reading ECU information such as part number, serial number and other settings engine such as temperature, pressure, battery voltage and so forth and on.
When you use the example LabVIEW VIs for the UDS protocol you have no need of the fields under Protocol for diagnostic.vi settings open except transmission and reception ID. (Normal - value ISP TP transport protocol)
After further reading on different ECU. I discovered this ID to pass - 7E0 and receipt ID - 7E8 are aone of the most common ID to connect with most calculators of major manufacturers such as Delphi.
What ID service you will find standard IDs based on Protocol NODES here. For the propreitery ID, you need help from manufacturer or Integrator.
http://www.neweagle.NET/support/wiki/index.php?title=Unified_Diagnostic_Services
Let me know if you have any questions.
Thank you
Vicky
-
Protocol Bluetooth Stack in LabVIEW
Hello
What I'm trying to do is to use LabVIEW on a PC with an attached Bluetooth dongle to talk to an owner designed Bluetooth device to connect with Bluetooth phones. I need the program to send some commands to the patented device, disconnect, then connect and talk to another device. The patented device that I want to connect is essentially just a server waiting for a cell phone to communicate with her. Once connected, garbage are exchanged between the phone and the device, and once authenticated, the Unit completed its function.
I've tested my Bluetooth dongle using the Simple Bluetooth Client.VI and the Simple Server.VI of Bluetooth running on two different PCs. They have been able to connect and transfer data properly.
My question arises, however, in LabVIEW allows you to specify a channel to connect via Bluetooth. The device patented essentially being a dumb device, she wants to follow the typical Bluetooth Stack Protocol and start once paired frequency hopping. He will not be able to devote himself to a single channel and frequency with the computer of pigs.
So I want to know is how LabVIEW treats the Protocol. The string that you specify in the VI Bluetooth actually affects the Protocol or that's just the way it communicates with the Bluetooth dongle? I have just need to know if LabVIEW supports already the Bluetooth protocol, or if there is a way around a dedicated channel. I want the computer to display and behave like a mobile devices view.
I read through several of the NOR tutorials, examples and discussion forums, but I couldn't find answers to my question. I could be missing something simple or easy here, but I want to assure you that it is still possible to achieve before I start to develop the code.
What I use:
LabView Full 2012
IOGear Bluetooth 2.1 USB Micro adapter
I must admit that I'm not the most technically savvy person when it comes to Bluetooth stacks and protocols, so please excuse mistakes with technical information, I could have. I must, however, work colleagues who are very experienced in Bluetooth (but not in LabVIEW), worry is not on the level of technical language that you use.
Thank you for your considerations in my problem. Do not hesitate to ask others (within limits reasonable owner) or clarification.
Kind regards
Bronson
bronsonmock,
The screws of LabVIEW Bluetooth and functions use RFCOMM, which is a connection protocol that exposes the Winsock interface. RFCOMM is a simple protocol that emulates communication series. The RFCOMM interface defines the clients and servers of Bluetooth.
Creating client applications and server Bluetooth in LabVIEW is similar to creating applications server and client for TCP communication. A Bluetooth Server uses the Protocol for discovery of Service (SDP) to broadcast the availability of the services on the server contains and listens to incoming connections. A client creates an outgoing RFCOMM connection to a server. Once the client and server connect to each other, they exchange data until the client or the server terminates the connection or the connection is lost.
Bluetooth of LabVIEW functions are really just a wrapper for the Windows bluetooth library functions. You can take a look and see how these protocols are processed to a lower level comprehension. I've also included this document where I shot the first two bits of information.
Use of LabVIEW with wireless devices:
http://zone.NI.com/reference/en-XX/help/371361J-01/lvconcepts/using_lv_with_wireless/
-
RT code works since the LabVIEW environment, but not when I create and deploy
I think there are a lot of reasons why this can happen, but I can't seem to pin one.
I have a classic controls program that runs on a cRIO. We recently decided to change the communication of a ProfiBus comsoft on Ethernet/IP card. (Industrial Protocol for Allen Renaud automata). For various reasons, we put the fuse in communication in the control loop.
Now when I run the LabVIEW now, it works fine. I can see data going to and coming from the controller. I can sniff packets and they look good. I get about 30 milliseconds on the loop, which is long, but since I am running in the IDE, I think is not bad. (In other words, I get data in and out every 30 milliseconds).
When I compile and set the binary on the cRIO, it breaks. I can still sniff packets, but what I'm getting now, is that all traffic to the controller of read requests. My write requests are missing. In addition to reading queries are poorly trained. Rather than ask 43 items in a table, they ask 1.
A test that I tried was to disable the read request. For the binary file, I don't see any traffic. For the IDE, I see write queries.
I use LV 2009 SP1. I have the version of NOR-Labs of the Ethernet/IP driver. (We have a request for a quote, but do not have the official driver.) In the meantime, faster I get this done, the happier everyone will be ;-)
Any suggestions?
Attention to the nodes of property which is usually my problem when it happens. Some who say they work in RT do not work in compiled RT
-
NEITHER TestStand Ethernet TCP/IP
Hello
I am looking to send packets on Ethernet TCP/IP Protocol,
Retrieve a possible answer and evolve the program that runs on TestStand according to return data.Would you have an idea of trigger tool (s) should I use?
ES what a DLL is sufficient?Kind regards.
Hello
You can do a step LabVIEW or CVI that use the TCP functions and recover data in TestStand in a local variable, for example. You can also make a dll from your source code pour can call it with TestStand.
Kind regards
-
Ethernet controller and network
I can't finde drivers:
My Network con:
PCI\VEN_168C & DEV_0036 & SUBSYS_217F103C & REV_01
PCI\VEN_168C & DEV_0036 & SUBSYS_217F103C
PCI\VEN_168C & DEV_0036 & CC_028000
PCI\VEN_168C & DEV_0036 & CC_0280
con Ethernet:
PCI\VEN_10EC & DEV_8136 & SUBSYS_21F7103C & REV_07
PCI\VEN_10EC & DEV_8136 & SUBSYS_21F7103C
PCI\VEN_10EC & DEV_8136 & CC_020000
PCI\VEN_10EC & DEV_8136 & CC_0200
I'm using 32 bit win 7 ultimate, laptop HP 15-G000SM
Hello:
You need these two drivers:
-
Connection ethernet or GPIB with Keithley 2612
Hallo
Here's my situation:
I'm relatively new to LabVIEW programming and want to install a configuration of measurement with LabVIEW and a SMU double Keithley 2612.
If I m work myself through Labview Beginners Guides and how to connect a measuring device with the first simple LabVIEW program.
Since I Don t own a GPIB-USB adapter for the moment, I was thinking of using Ethernet for the EMS connection that gets ist own IP address. The connection to the PC works and SMU SMU ethernet can be remote controlled.
Here's my problem:
I can´t find (usable) guides for the installation of LabView via Ethernet.
My 500 pages book 'Introduction to LabVIEW' (as of 2009) doesn´t have even a hint for an ethernet connection, while the GPIB, RS232 and CAN are covered pretty well.
Here's my question:
Should I continue to try to get LabVIEW working on Ethernet, or would it be better to buy a new adapter USB GPIB.
Does anyone know good Howto for creating Ethernet connections?
Should I just the bad 'Introduction to Labview?
The use of Ethernet has disadvantages compared to the GPIB-USB?
I'm happy to answer additional questions.
Thank you.
Download the Labview driver for the series of 26xxA from Keithley web site.
For a Visa resource string use something of the form: "tcpip::aaa.bbb .ccc. ddd::instr" where aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd is the ip address of the instrument that you can get through the façade or run MAX and auto-le discover.
When you finally get a USB-GPIB converter all you have to do is change the resource in the form of gpib string: GPIB::XX:instr «»
-
Error executing ethernet modbus slave demon in an executable
I wrote an application that integrates a modbus ethernet slave - similar to that included in the examples of LabView (2013). If I run this as a VI, then there is no problem. However, if I create an executable file then I get an error message on the version of demon slave being too old to convert it into 2013 version 8.6. I use NI Modbus Library 1.2.1 and the 86 folder.
To isolate the problem of modbus to my initial request, I took the slave example LabView MB Ethernet (2013) and launched a project which includes the demon slave vi and the vi.lib modbus 8.6. I changed the path to the slave demon in the example of the slave so that it points to the location of the slave vi demon in my project. If I build the application and run it I get a slightly different error - "the demon slave vi is not executable.
I don't understand why the demon of the slave will not run an exe program but will be in a VI.
This error does not much sense. LV 2013 can certainly open and run LV8.6 files.
You said that the executable file it who gives you this error. When you run this executable? It is on the same PC, you have developed and created the .exe on? Or another PC?
I wonder if you run it on another PC, you do not have the runtime engine proper installed.
In addition, once you moved the VI Modbus to your most recent LV2013 environment, you've been through and mass compiled this library?
-
faster data transfer on ethernet
Hi friends,
I use VISA for instrument control via ethernet tcp/ip Protocol.
the application is written in VB6 with the help of measurment studio controlsI need to read the data of the large array, element by element, since the insrument has no transfer block function
It takes too much time to read the entire array.
the thing that I observed, was there a lag of 100mSec between Visa write and read of Visa (Visa read answers back after 100msec)
what I've observed with the help of NOR 488.2 SPY.(this problem was not observed when checking the Visa-free)
y at - it an explanation why this delay 100msec is coming for each reading, which equals a huge time for 30,000 FlexChoice read.
Magali
Most of the standards for VISAS is set to optimize for wholesale transfers in bulk, since it is the standard for TCP/IP instruments. If you are transferring small amounts of data at a time there are several properties/attributes that you can change to get better performance. Open the VISA help and take a look at the following attributes:
VI_ATTR_SUPPRESS_END_EN
VI_ATTR_TCPIP_NODELAY
VI_ATTR_TERMCHARMost probably you will need to just change the first two, because your instrument probably does not support any type of stop character.
-Josh
-
I have a question regarding the Protocol address resolution.
Suppose that a network device enters a network where the trafficking involves UPnP messages among other things.
How the device will start its cache ARP Table fill?
My understanding is that the following sequence takes place...
1. the unit can receive a UPnP discover message, it must take into account.
2. now, he already has the MAC address of the bridge while attribution of IP through DHCP.
3. it sends a response to the entry door, because he does not know the MAC address of sender tha of the UPnP message.
4. the bridge takes care to send the message to the destination MAC address.
5. after sending the response, the device to update its ARP table by sending ARP messages to the sender of the previous UPnP message.
I hope that I don't confuse anyone!
Basically any network device that I'm trying to ask is do an entry in its ARP table before you reply to the sender of a message to the network?
Or she will leave the bridge deal with it and take care of the ARP table entry later (see above)?
see you soon,
Gandalf
I don't see the contradiction between 2 and 4. One is for the unicast and the other for the multicast/broadcast. Suffice to say, that a computer that receives something captures the information contained in the ARP table.
He enters information in the ARP cache because that's how it works. Remember that the ARP and the management of entire ARP cache is at a very low level in the communication stack. All of the ARP is located somewhere in the "context". Programs only communicate using the intellectual property and will just send something to an IP address. Everything, that is, ARP, routing, etc. is done automatically in the operating system.
Of course, it can always be that the person who receives something has no answer. But how the Protocol IP or ARP knows he won't? It is much easier and faster to store the information anyway. It is stored for 5 minutes. If this is not necessary it won't really hurt. If it is necessary it is already there and should not start another ARP request to find the MAC address of the original sender to answer now. For example, you store information that you have learned. You store the information if you receive an ARP request for your IP address, and in other cases.
With regard to the last question: it depends on what is the 'message '.
All communication over ethernet (wired or wireless) using MAC addresses. Always. It matters little whether unicast, multicast, or broadcast. The latter two uses special MAC addresses, but that's all. An ethernet frame always contains an address MAC of the sender and the receiver. Always.
Frames Ethernet with any protocol you like. If it contains no IP packets, there are no contained IP addresses. If it contains an IP packet there are IP addresses.
Thus, a multicast ethernet or broadcast may or may not contain IP addresses according to what is content. If this is not IP there is no IP address
Any communication using IP (regardless of the Protocol below) has IP addresses. It matters little whether unicast, multicast, or broadcast. An IP packet always contains the IP address of the sender and the destination. broadcast and multicast addresses are just special IP addresses.
When you send IP through an Ethernet the image on the thread will contain the IP address and MAC. When you send the IP through a network ATM frames will contain the IP and ATM addresses. IP and 'carrier' protocol that is used on the physical media connecting the two devices are entirely independent.
Of course, the most common installation in a House that LAN (many other sources) is usually a LAN ethernet, which means that you are running IP over ethernet within your local network.
-
Closing datos por en scada modbus
Muy buen dia a todos.
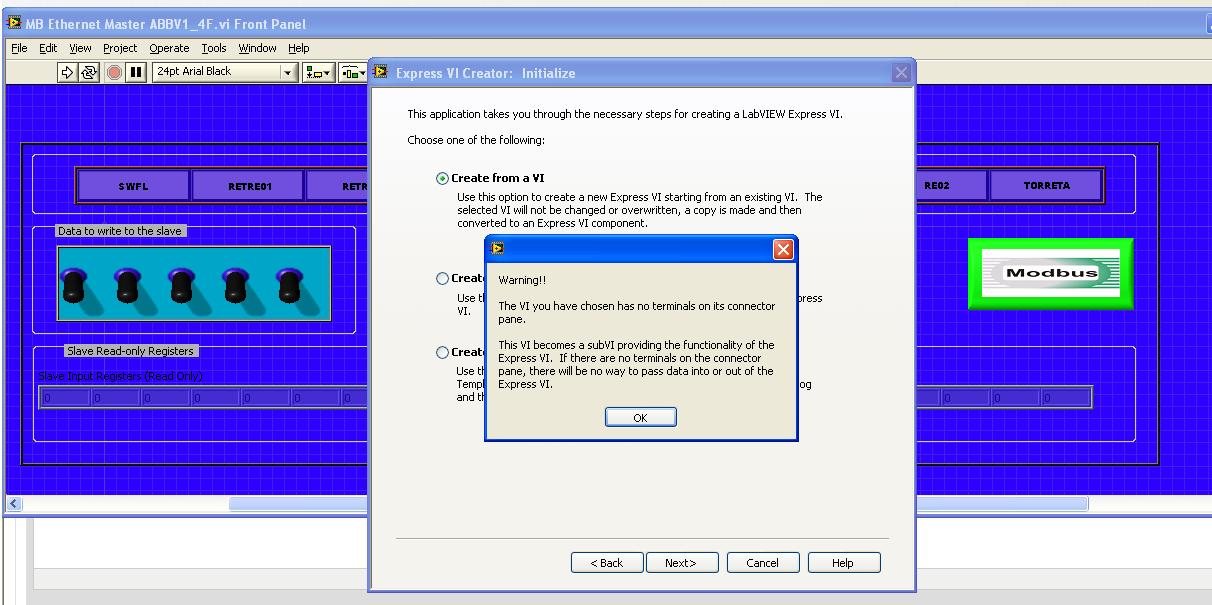
Estoy modificando UN SCADA in the empresa in donde trabajo pero el problema as hay are consta esta para trabajar con FIELDPOINTS, yo eliminate los fieldpoints u OPC powered through y con PLC of MODBUS TCPIP similarly o serial ABB. Comunicación is the prevalence, puedo leer y señales analogicas write y digitales pero el escollo librar trato're como VI individual intensification has the perfeccion, pero ago al of integrarlo hora of SCADA no works, me errores marca el as como modulo escritura y lectura modbus esta receiving characters no aceptados o things asi extranas, estos momentos estoy tratando crear a Subvi don't express pero no is como hacerlo , is that the of primero doy a tools y ahi in crear una nueva express vi, of doy NEW despues en CREATE from a VI selecciono mi VI y me appears lo siguiente:
SE me hace porque mi vi tiene tickets extraño y salidas, in this case tickets las salidas St o o reels pero no be that pasa.
También estoy intentando hacer algo con las share if is you can hacer algo pero tampoco, en so mi problema're than mi SCADA y MODBUS corran al mismo tiempo, tambien initiates include todo el vi in SCADA el plano y cuando llega el programa ahi flow to para todo, ahi is is, variables, supuse than era una structure while , is the altogether there are quick-witted pero solo is me da UN valor.
Ojala me can help alguien esto is to give has a client unos dias UN y todo esta por eso paradox.
Mucho thank knew tiempo, reciban a cordial saludo.
ING. A. Abraham. Alfonseca Melendez
Normal
0fake
fake
fakeEN-US
X NONE
X NONEMicrosoftInternetExplorer4
/ * Style definitions * /.
table. MsoNormalTable
{mso-style-name: "Table Normal";}
MSO-knew-rowband-size: 0;
MSO-knew-colband-size: 0;
MSO-style - noshow:yes;
MSO-style-priority: 99;
MSO-style - qformat:yes;
"mso-style-parent:" ";" "
MSO-padding-alt: 0 to 5.4pt 0 to 5.4pt;
MSO-para-margin-top: 0;
MSO-para-margin-right: 0;
MSO-para-margin-bottom: 10.0pt;
MSO-para-margin-left: 0;
line-height: 115%;
MSO-pagination: widow-orphan;
font-size: 11.0pt;
font family: 'Calibri', 'sans-serif ';
MSO-ascii-font-family: Calibri;
MSO-ascii-theme-make: minor-latin;
mso-fareast-font-family: "Times New Roman";
mso-fareast-theme-make: minor-fareast.
MSO-hansi-font-family: Calibri;
MSO-hansi-theme-make: minor-latin ;}Hola Abraham, the advantage of
comunicarte con directly los lugar por MODBUS FielPoints are that the communication
haces el through pilot directly variables compartidas, ahora o
con estos tambien you puedes Comunicar por MODBUS. Para con MODBUS communication
Server i/o MODBUS to estas using el este esta LabVIEW RT o en LabVIEW DSC, o
the MODBUS libreria utilizando estas. ?Ahora el error that you
Genera el del VI Express are you porque VI not las tiene nada en contacts
Terminal, an esto is refiere don't con as no tickets tiene y salidas. Ahora
probably aqui no using screw Express, the utility of los need live
Express General are building as despues con use en herramientas para
Los programas mas than fr if a component in a specific en programa, y proven
MAS well utility para el Worflow para el programa final.Ahora el problema aqui of
No funcionen juntos can be much more than a problem of integration. Como so
mencionas you colocas a Subvi, con a ciclo while inside of a VI, VI el
main goes a detenido meet (o por lo menos el ciclo in el as metiste
Este Subvi) terminen run one until. Quitar el ciclo Al solo everything is
runs una vez cada vez lo controls has call desde el principal, so solo lo
Mandas call una vez solo you will a dar UN dato.Ahora lo mas algo
con el to use are simple as puedes hacer I/O Server in case of than cuentes
El, there is what sets el I/O server variable ligar puedes compartidas has los
looking for MODBUS, y como utilizarlos compartidas variables in you sistema
SCADA.Estas ligas you pueden ser
utility of:Connected LabVIEW has any red Industrial y PLC.
Developer Zone - National InstrumentsHow to turn an RT target in Modbus slave using i/o
Servers - Developer Zone - National InstrumentsConnected LabVIEW has any red Industrial y PLC.
Developer Zone - National InstrumentsSaludos
-
Hello
I do test with NI Veristand HIL. My hardware is a cRIO 9075 siemens AND 200 s PLC. I found an address ethernet/IP add it to veristand:http://zone.ni.com/devzone/cda/epd/p/id/6337
However, if I understand correctly, it will not work with siemens plc. Are there patterns that I can do on the add-on ethernet/IP, which allows to work on siemens PLCs?
any help is deeply appreciated.
Do not confuse Ethernet/IP (Ethernet industrial Protocol) with "Ethernet" (the physical layer, it is built on). Both Profinet and Ethernet/IP are protocols built on top of the Ethernet physical layer, but apart from that, they are completely different protocols.
Regarding your question, NI VeriStand consists of a runtime of models yout, IO, etc... and an application for configuring host-side and communicates with the engine. Generally, the engine will run on a system in time real (for example a CompactRIO or PXI system), but it is also possible to run the engine on your WIndows machine. The downside to this is that Windows is not a real-time operating system, so you can't wait operation is deterministic, free of jitter, which is usually required by the test of RT applications.
Insofar as the implementation differences, your target cRIO runs a VxWorks operating system, which is unable to call DLLs. Instead, you'll have to comile your models in a .out file. If you use the Mathworks Simulink®, NI VeriStand comes with a .tlc of VxWorks file that can be drawn from the real-time Workshop. If you compile your own C-base model, you will need to use the chain for VxWorks GNU tools. You can find instructions on how to do it here.
If you use the cRIO VeriStand engine, you will need to use a C series Profibus or Profinet module for communication with the controller. I don't have any experience with these, but you need to program the FPGA and probably write a device customized to interface the NI VeriStand code. If you use the Windows engine, there may be 3 third-party drivers available for this type of communication that you could then conclude with a custom device.
-
Servos and HC-SR04 in a code (arduino)
Hi guys,.
How can we use servos and HC-sr04 in the same code?
I'm in a situation of catch 22 where I can't use both of them as LINX supports HC-SR04 but no servos, LIFA media servos but not the HC-SR04.
I am stuggling to make a Subvi pulseIn for this.
Is there any solution for this?
It's the easiest way to do it! In fact, the hardest part is written the Arduino for the custom code. From the link I sent you, there's a Subvi, which already exists to invoke the custom command you defined.
The toolkits Arduino, both work in the same way - you run a firmware pre-compiled on the Arduino which is the interface between the hardware and it speaks to LabVIEW using a protocol series. The Toolbox said, you don't need to write LabVIEW code for the serial Protocol, nor do you need to write the Arduino Sketch yourself. The fact that you can change the sketch to add custom commands is a very powerful feature and saves you more having to write your own sketch (or LabVIEW code) from scratch!
-
Scan engine mode on RT does not not with EtherCAT NI 9144 chassis
Hello
I have problem with communication of the cRIO-9074 RT with NO 9144 via EtherCAT.
I add the expansion with a NI 9203 module chassis to my system running on the cRIO-9074.
I use it in engine scan mode. My PC application communicates with RT by network data stream. When I run only asks to RT, the RT is the reading of variables EtherCAT I/O chassis with no problems, but when I run the PC host application, RT probably go into configuration mode and interrupts communication with chassis EtherCAT - I can see that the LAN LED on expansion chassis stops flashing. "" Then, with still running application I click in the LabVIEW Project Explorer, the item target and select utilities ' Mode Scan Engine "pass back"Switch to active"Configuration, then it starts to communicate. I tried to do the same thing programmatically work with the Scan Engine VI Mode Set but it doesn´t so Runt-time it does not work as well.The behavior described above happened when I added the chassis extension in the project and only the module place entries in this chassis are affected, the rest modules 8 places directly in the cRIO-9074 work withou any problem.
System:
Professional Win7
LabVIEW 2013 SP1
OR-Industrial Communications for EtherCAT 2.7
OR CompactRIO 13.1Hello
problem solved. The reason was function RT Set Date and TIme.vi what casues on NOR-9144 error and blocked EtherCAT communication. I found that this function is no longer supported in LabVIEW. After the removal of this feature of application of RT, everything works fine.
BR, Jan
Maybe you are looking for
-
Updated Snow Leopard to Yosemite now (may 2016)
-After years of use of Snow Leopard on my iMac 27 "10.6.8, I've upgraded directly to El Capitan. -No problem to do so. -When you use El Capitan, I encountered several problems (unsupported software and hardware). -J' therefore decided to install Yose
-
everything looks ok, but when I print the paper passes through the printer but nothing prints, suggestions. worked fine until today after a move
-
There are a lot of software programs out there free download of advertising. The problem is after they scan your pc for the questions then they want you to pay to fix them. Y at - it software that will scan and fix your pc for free?
-
Windows Explorer search feature does not work on a PDF file
I've upgraded to WINDOWS 7 this month. As in the past I am still investigating several cases filled with PDF files for specific strings in the PDF file. The new feature of windows search is not finding files. I have all the indexed folders and have p
-
BlackBerry 8330 Smartphone screen is dark & blink red (4blinks)
My 8330 screen is dark and I'm lit or flashing red signal. I tried pulling the battery to reset and does not help. Can anyone offer any suggestions? Thank you JRW8