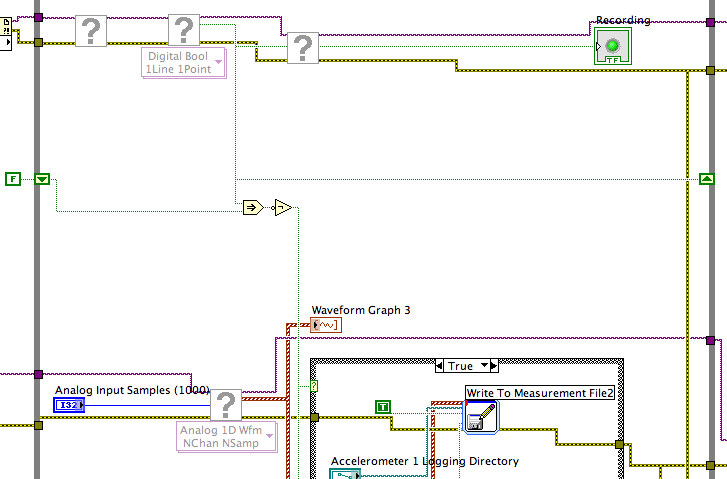
Lose the analog input samples to the high recovery rate?
I got it. I changed to a life-long.
I then changed code so that I was counting the samples collected in the software and stops when I had them all. Previously I was following the task of tension HAVE with the Done.vi of task completion is DAQmx.
Tags: NI Hardware
Similar Questions
-
lose the function of F11 Recovery Manager
Dear Sir.
I have narrowing of drive c and lose the F11 Recovery Manager functionality. I'm worried that now what I'll do to retrieve this function.
answer me as soon as possible.
Thank you
1 u get backup data, then you can run the recovery dvd, if it was not created by u, then you can create it using recovery manager. After factory reset you will be able 2 Use F11 Recovery Manager features
-
What is the minimum response of analog input, through DSP online, output analog time?
Hello experts!
I want to know if it is possible to get a very quick response latency (~ 1 ms) sound recording (analog input), through online registration (DSP online), the presentation of his (analog output) processing, by using the DAQmx programming codes. My system of NEITHER includes NOR SMU 8135, SMU 6358 DAQ Multifunction controller and SMU 5412 arbitrary signal generator. I also have access to the latest version of Labview (2015 Version) software.
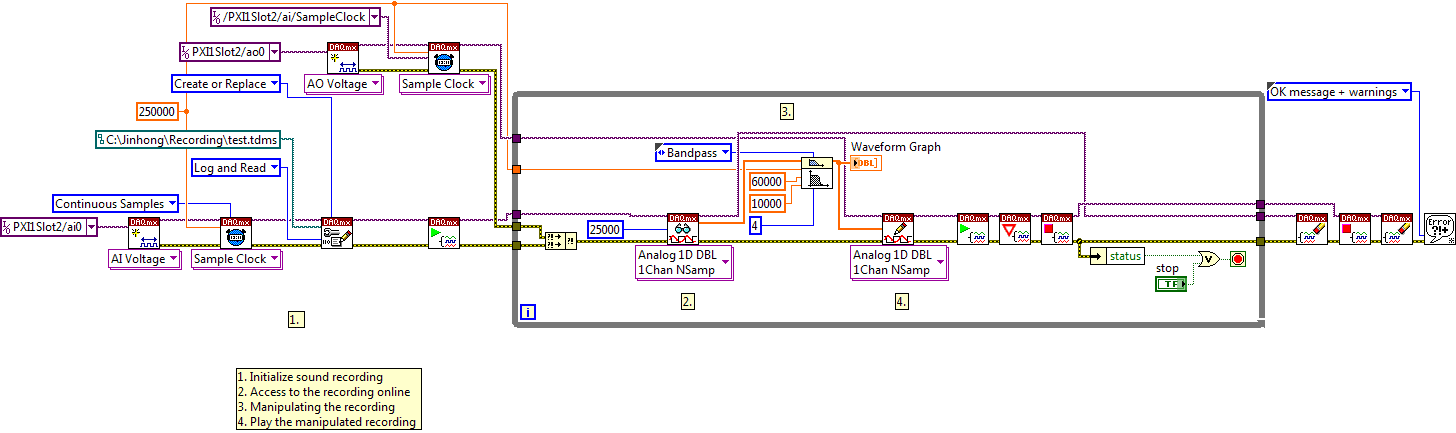
My project is on auditory disturbances, which inovles record vocalizations, manipulating the recorded vocalziations and then present the manipulated vocalizations. My current idea of how to achieve this fact triggered output voltage after reading the input using DAQmx Read samples. DAQmx Read output is filtered online and then passed as input for the DAQmx writing for analog output. For purposes of illustration, examples of code are presented below. Note for simplisity, codes for the trigger part are not presented here. It's something to work in the future.
My question here is If the idea above should be reaching ~ 1ms delay? Or I have to rely on a totally different programming module, the FPGA? I am very new to Labview so as to NEITHER. After reading some documentation on FPGA, I realized that my current hardware is unable to do so because I do not have the FPGA signals processing equipment. Am I wrong?
Something might be important to mention, I'm tasting with network (approximately 16 microphones) microphones at very high sampling rate (250 kHz), which is technically very high speed. Natually, these records must be saved on hard drive. Here again, a single microphone is shown.
I have two concerns that my current approach could achieve my goal.
First, for the DAQmx Read function in step 2, I put the samples to be read as 1/10 of the sampling frequency. It's recommended by Labview and so necessary to avoid buffer overflow when a smaller number is used. However, my concern here associated with the latency of the answer is that it might already cause a delay of 100 ms response, i.e. the time to collect these samples before reading. Is this true?
Secondly, every interaction while the loop takes at least a few tens of milliseconds (~ 30 ms). He is originally a State 30 late?
Hey, I've never used or familiar with the hardware you have. So I can't help you there.
On the side of RT, again once I don't know about your hardware, but I used NOR myRIO 1900, where he has a personality of high specific speed for the RT where I can acquire the kHz Audio @44 and process data. Based image processing is ultimately do the treatment on a wide range of audio data you have gathered through high sampling frequency and number number of samples as permitted by latency, please check this .
I lost about 2 weeks to understand host-side does not work and another 2 weeks to understand the even side of RT does not work for online processing (real time). Then, finally now I'm working on FPGA, where the sampling rate is 250 kHz (of course shared by multiple channels).
The complex thing with FPGA is coding, please check if the filter you want is given below as labview automatically generates some codes of some filters.
Most of them will work in 1 SCTL IE if your target has 40 MHz clock algorithm will run in 25 ns. That's what I was looking for, I hope you

See you soon... !
-
Save the high sampling rate data
Hello!
I use NI PXI-4462. (204.8kS, input analog 4 / s sampling frequency)
I want to collect data from "load" (channel 1) and "acceleration sensor" (2nd, 3rd, 4th channel).
I also want to save data to a text file.
So I do a front pannel and block diagram. You can see in the attached file.
The program works well in a low sampling rate.
However, when I put up to 204800 s/s sample rate, the program gives me "error-200279".»
I don't know what means this error, and I know why this happened in the high sampling rate.
I want to know how I can fix it.
Is there any problem in my diagram?
Is it possible to save high sampling rate data?
I really want to samplling more than 200000 s/s rate.
I would appreciate if you can help me.
Thank you.
NH,
You have provided excellent documentation. So what has happened is that the amount of time it takes to run the other portion of the loop results in a number of samples to be taken is greater than the size of the buffer you provided (I don't know exactly what it is, but it will happen at high frequencies of sampling high) resulting in samples are crushed. You might be best served in this case to take a loop of producer-consumer - have the loop you have acquire the data but then have an additional loop that processes the data in parallel with the acquisition. The data would be shipped from the producer to the consumer via a queue. However, a caveat is that, if you have a queue that is infinitely deep and you start to fall behind, you will find at the sampling frequency, you specify that you will begin to use more and more memory. In this case, you will need to find a way to optimise your calculations or allow acquisition with loss.
I hope this helps. Matt
-
Questions about the synchronization between output and analog input
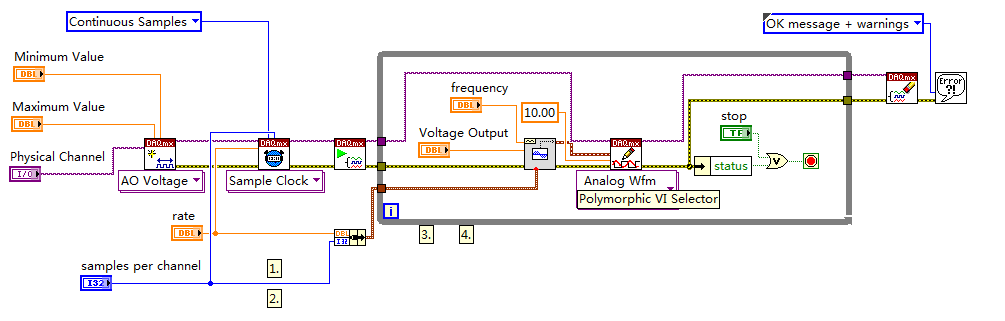
Hi all
I now have a simple task which head a signal voltage (from PXI ao0) on a circuit and then your comments a voltage at the terminals of a component, for example, that one of the resistors in the circuit, through ai0 on PXI. So in this case, the synchronization between analog input and analog output must be made to avoid error of phase shift.
I tried to build my VI by learning this example: https://decibel.ni.com/content/docs/DOC-3882
However I have a few questions.
1. I noticed that there is a merged error fed the "start task" sub VI for the analog output. What is the point of fusion to mistake?
2. I enclose my VI (also shown below) for the output voltage. I put my writing of DAQmx Subvi in the while loop so that I can change the voltage while the VI is running.
However, in the example, the author has been reading outside of the loop and before even the start task. What difference will it make?
3. I have also attached my synchronized VI. I always put the wavegeneration and the DAQmxwrite in the loop. A bulging guard error saying about samples is not available and needs to a higher sampling rate or a longer wait time. What causes this?
I appreciate that these problems can be solved. Thanks to you all.
(1) first you need start the task of acquiring, he'll wait for trigger here. And then you start the build task that provides this trigger. If acquisition could trigger and never start.
(3) you must first write something in the buffer (writing DAQmx), then only you can generate it (Daqmx Start).
Check Cont Gen tension Wfm - Int Clk - no Regeneration.vi in the help-> examples for example.
-
read the multiple analog inputs at the same time
Hi all
I use USB-6001 and want to develop an application to multiple tasks in C++. I try to read several analog inputs at the same time, but got some errors. To put it simply, I copy one of the sample code to read in analog data in a channel, and then turn it into function. Then I call this function to thread with the names of different poles (for example Dev1/ai0, Dev1/ai1) and I come across this error:
"The specified source is reserved. The operation can not be specified such complete"code of State-50103
I have search the forums, this may be because I use the hardware timing in this function, and this material timing cannot be used simultaneously by multiple tasks. I may have to put all the lines, I want to read in a single task (such as Dev1 / ai0:1). This way I can read two lines at the same time. However, when I try this, I encounter another error:
Status code "buffer is too small to contain the data read" - 200299
So here is my question, what should I do if I don't want to read the multiple analog inputs at the same time? Is the thing that hard time cannot be used by several true task? If I have to read several lines to a single task, how to set the settings?
-
Several analog inputs seem to change any of the other (details DAQ: 2120 BNC and 6062E)
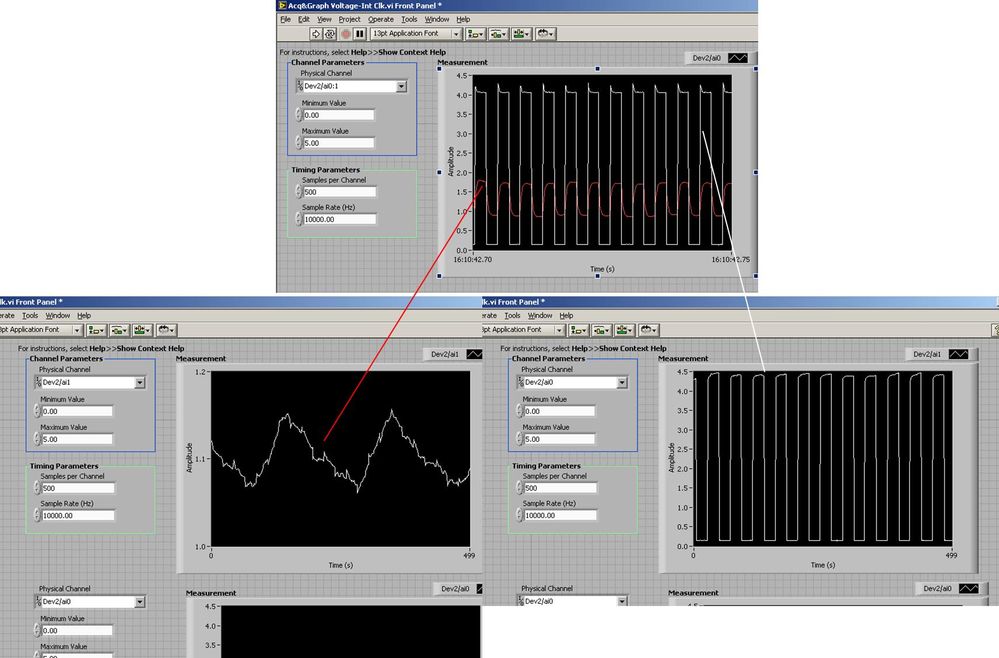
I use the BNC 2120 DAQ board connected to the data acquisition card 6062E to record two analog inputs. An entry is connected to ai0 and the other at ai1. Example vi: "Acq & graph int clk tension" has been used to measure the two entries with the value read NChan NSamp vi (channels being dev2 / ai0:1). The output is the top graph in the image. However, this seemed a bit strange to me that one of them should be modulating with a different frequency. When I record both entered individually (two in low pictures) they are indeed different since the entries shown in the top graph.

Why this would be the case, and how can I overcome this to measure the real signals?
Thank you!
The E series card takes the samples as soon as possible. Thus, for example,.
If you have 16 analog input channels but you only read of
channel 0 and 1, the map will show the channels 0 and 1 right
After and then wait 14 'ticks '. What's that little run-in
the origin of the afterglow.
I think you can get the card to wait a certain
number of ticks with a property node. I have attached a screenshot. You
can find the property node in the palette of functions >
Measurement of e/s > NOR-DAQmx > node Timing. Expand it
Property node so there's two entrances. The properties are in
Left click on the node and going more > converted >
Its properties delay units and sampling clock delay and delay that
you want.If the phase is important so the above is not the best
the option because it causes a delay in phase. So, if you need true simultaneous
sampling, then you will need different hardware. The S series is everything
simultaneous sampling.Or, rather than the Delay property and delay units, try the Rate property
find more > converted > rate.If this is not
work either, you can move the second signal source to, say, AI8 and
Connect everyone to the ground. Readings for these, but just do not take into account
the data. In this way the ADC will sag to the ground at the time where that can happen
the second string in the way so that you should not see this frequency
ghosting on the other channel. -
PXI-6071e offset drift on the analog inputs
Hi, I have three cards PXI-6071E, sitting in a PXI-1042 chassis that is controlled by a computer with windows XP. The 6071Es are connected to the SCB-100 break out boxes that are wired to a pannel of BNC female Panel Mount on twisted pair.
I noticed that all of my analog inputs will drift around-10 V to + 10 V if they are not connected to what whether forcing them to a certain tension. This has always happened. We also see a bit of crosstalk between channels. For example if I open a panel of test in the measurement and automation Explorer I can watch the voltage read on the drift tickets through their full range, and alteration of the signals on nearby channels will appear on the channel, I am able.
Is this just standard behavior and to predict? Is there something more I could do to minimize this drift and crosstalk? I am trying to reduce noise in my system so I figure optimize my DAQ could not hurt.
Thank you
With nothing plugged into the catch to high impedance, drifting you see is quite normal. The front end of the circuitry builds up a charge, crosstalk is proabably due to the multiplexer input (did not check but I think that the 6071 has a) transferring the load to the other channels when they are analyzed.
Search the Forum of ghosting, you will find related discussions.
-AK2DM
-
I use an analog input on a PCI-6224 and are having problems with the clock source
I use an analog input on a PCI-6224 and are having problems with the clock source. I'm trying samples of 16 different analog inputs very quickly. I have the sample mode: Timed Single Point material. The rate, that I am running is the maximum (250 kHz (15625Hz per channel)). I left the default clock source and trying to taste several times. The analogue input works for a short time (2-3 seconds) and then everything stops. I'm doing something wrong or is there something I'm missing? Any advice would be great.
That's how you samples using the sample clock clock. If you see a delay then something is wrong with how you track/data visualization.
Single point NI the hardware is for PID control with a real-time operating system.
-
Problem with a digital output in the information of an analog input
Hello
I use a SCXI-1000DC module with a module of the SCXI-1600, SCXI-1531 module and SCXI-1163 module to receive an analog of an accelerometer signal and a digital signal.
I claim that the accelerometer is constantly monitored, and the output is on when I want to, by an impulse that I comand in labview.
I use a rate 25 k and a 12, 5K samples per channel on DAQmx Timing.I notice in DAQmx read, if I put a sample of hight by channel, the output is not there when I want to, and if I put a few samples per channel, I exit when I want to, but the program seems to be slow with the passage of time. I don't know how I can solve this problem!
I'm sorry for my English, and I hope you can help me.
Thank you
Silvia
Hello Silvia,.
If you ask a larger number of samples, the labview diagram will stay longer in the DAQmx Read function, so the while loop runs slowly, and the digital output is updated less often.
I suggest that you use 2 separate while loops: one for the analog input and the other for digital output, so that each loop might run at a different speed.
Best regards
-
15-20 time of latency to see the changes in analog inputs
I inherited a program extremely complex. I find that I see 15-20 seconds latency on the changes to the analog inputs. I can't post the code - (it has more than 200 sub screw) but I have captured the relevant section in the long latency period of the changes.jpg of analog input attached.
I tried to change the sampling rate and see the same problem from 1 Hz to 25 Hz (limit of reliable sampling with this PC). I'm looking at indicators which are directly related to the acquisition of data Read.vi as evidenced by the big red arrow.
I modeled the nested struct in the template attached without latency problems.jpg. There is no perceptible latency but it duplicates the nested structures.
The only thing not shown is that there are several cases of Read.vi of data acquisition using the same physical changes but not of them are in the loops that need to run at the same time.
The data are consistent with the entries, just delayed.
The Signal processing device is a USB-6343. I am running these screws on LabVIEW 2011 edition.
Any ideas?
Yes, instead of getting just 1 sample buffer, try to get all the samples.
Then you can retrieve the most recent example of all the samples you get and take the rest of them.
Or you can change the configuration of taks for only once every time that you call the read function.
-
Read the counter timeout in synchronized to count-analog input
Ciao, Giovanni.
The two tasks are run in parallel so there is no guarantee which task starts first. I suspect that when you are away from the counter samples, it is because the task of analog input before starting the task of counter. In this case, the task of counter would be ready to accept examples of clock and may be missing some edges of the clock at the time wherever he is started.
One way to solve the problem would be to use the wires of the error in order to ensure the time started the task of counter in front of the task of analog input. You can also use a sequence structure to do that.
The counter is sampled on each edge of the sample clock HAVE no matter what you set the 'rate' of entry to the. When you use an "external" clock (external to the task that is), the driver uses just the entry rate to set some default parameters (size of buffer for example).
If you have any questions, feel free to ask!
Best regards
-
Toggle the analog inputs and tasks of output on the same card in LabView
Hello
I'm relatively new to LabView and am trying to find the best way to switch between reading and writing tasks on my PCI-6024E. It seems this would be a common thing to do, but I found no good documentation or any relatable example program. Basically, I would like to be able to monitor certain analog inputs and then write that some outputs if an entry is in accordance with certain specific conditions (say > 4 Volts voltage). It is my understanding that you can only signal (input and output) types associated within a single task in DAQmx. I also understand that you cannot have multiple tasks running at the same time on the same material/map, otherwise you get a: 50103 error 'The specified resource is reserved. Calendar is not really all that matters to me, but quite synchronous and effective would be nice.
I have attached a sample program that shows more or less what I'm trying to do. I want to follow several analog input lines (AI0 AI1, AI2 and AI3 and) effectively at the same time. If certain conditions are met, AI3 > 4 Volts, then write 5 Volts for analog AO0 and AO1 outings. I also want to maintain output at 5 Volts up to AI3 falls below 4 Volts. Is there a better way to pass the task to read and write than what I've done here? In a sense, all I really do is toggle of a state machine if the required conditions are met and if start/stop tasks of reading/writing necessary.
One last question, is there a way to display the four channels in the waveform graph using the 1 d NChan 1Samp mode so I can have a time chart and indicators?
P.S. I'm under LabView 2011 on Windows 7. Your ideas and suggestions are appreciated.
Thank you
KJ
I also understand that you cannot have multiple tasks running at the same time on the same material/map, otherwise you get a: 50103 error 'The specified resource is reserved.
This is incorrect. You can't have two tasks of the same type running on a single card. You can have an analog input and analog output task running simultaneously on the same hardware.
You are right that each task can have only one type of task (entry or exit). Discover DAQmx examples in the example Finder to get examples of synchronized input and output.
PRO TIP: In the Finder of the example, go to the drop-down list in the lower left corner. Pull down and select Add Hardware. In the pop-up window, add your PCI-6024E to the right pane. Click OK in this window. Then in the main window of Finder example select your hardware from the drop-down list and check the filter results by the hardware. The example Finder then only you will show examples that are out-of-the-box compatible with your hardware. I am sure you can find something to fit your needs here.
-
How do I get the analog input signal and send it to output analog (real time)
Hello world
I do a simple task in Visual C++ and I use PCI-6221(37 pin).
Basically, I want to send the same signal of "analog input" to the "analog output".
at the same time (or almost), to make real-time application.
Can someone provide me with sample program please.
I would be grateful if you could provide me with the great tutorial that explains
step by step everything about NOR-DAQmx for C/C++ programming.
Best regards
Khassan
This is my code in C++, you can optimize it if that seems too messy. This code reads the analog input signals and exports it through the analog outputs.
To make this code additional work of the directories include and library directories must be added to OR.
I hope it helps someone.
#include
#include
#include "NIDAQmx.h".
#include#define DAQmxErrChk (functionCall) {if (DAQmxFailed (error = (functionCall))) {goto error ;}}
int main (int argc, char * argv [])
{
Int32 error = 0;
TaskHandle taskHandleRead = 0, taskHandleWrite = 0;
Read Int32 = 0;
float64 context [1000];
char errBuffRead [2048] = {'\0'};
char errBuffWrite [2048] = {'\0'};
bool32 done = 0;
Int32 wrote;DAQmxErrChk (DAQmxCreateTask("",&taskHandleRead));
DAQmxErrChk (DAQmxCreateAIVoltageChan(taskHandleRead,"Dev1/ai0","",DAQmx_Val_Cfg_Default,-10.0,10.0,DAQmx_Val_Volts,NULL));
DAQmxErrChk (DAQmxCfgSampClkTiming(taskHandleRead,"",100.0,DAQmx_Val_Rising,DAQmx_Val_ContSamps,0));
DAQmxErrChk (DAQmxCreateTask("",&taskHandleWrite));
DAQmxErrChk (DAQmxCreateAOVoltageChan(taskHandleWrite,"Dev1/ao0","",-10.0,10.0,DAQmx_Val_Volts,NULL));
DAQmxErrChk (DAQmxCfgSampClkTiming(taskHandleWrite,"ai/SampleClock",100.0,DAQmx_Val_Rising,DAQmx_Val_ContSamps,1000));DAQmxErrChk (DAQmxStartTask (taskHandleRead));
DAQmxErrChk (DAQmxStartTask (taskHandleWrite));While (! fact &! _kbhit())
{
DAQmxErrChk (DAQmxReadAnalogF64(taskHandleRead,1,10,DAQmx_Val_GroupByScanNumber,dataRead,1000,&read,));
DAQmxErrChk (DAQmxWriteAnalogF64(taskHandleWrite,read,0,10.0,DAQmx_Val_GroupByChannel,dataRead,&written,));
}
_getch();Error:
If (DAQmxFailed (error)){
DAQmxGetExtendedErrorInfo (errBuffRead, 2048);
DAQmxGetExtendedErrorInfo (errBuffWrite, 2048);
}
If (taskHandleRead! = 0){
DAQmxStopTask (taskHandleRead);
DAQmxClearTask (taskHandleRead);
}
If (taskHandleWrite! = 0){
DAQmxStopTask (taskHandleWrite);
DAQmxClearTask (taskHandleWrite);
}
If {(DAQmxFailed (error))
printf ("error DAQmx: %s\n",errBuffRead); ")
printf ("error DAQmx: %s\n",errBuffWrite); ")
}
printf ("end of the program, press the Enter key to quit\n");
GetChar ();
return 0;
} -
Registration of the analog inputs in continuous (Clipping)
Material:
(1) USB NI CDaq-9174 chassis
(2) NEITHER 9234 Analog Input Modules
(1) digital input module 9402 OR
Goal/Requirements:
To read the analog inputs continuous only in digital input is "high".
Problem:
Timestamp in log file prooves that logging is not continuous. It seems that the first seconds of 0.6 of every second is recording, I guess the other 0.4 is used to write custom? I can't use VI SignalExpress for this application because logging must be triggered by a high digital input.
File is attached. Thank you all!
To detect changes in the digital input, you need to compare the current value to the previous. The easiest way to do this is to plug the output of digital playback on a shift register. The Boolean function involves will tell you when a transition has taken place. See the central part of the image below. If you exchange the true and the false case of case structures, you not the inversion function. Look at the help file for more information on what the function actually implies.
You must also change the wiring of the name of input for writing custom file FIle.vi so that the name is automaticlly changed. Depending on what you want the naming system to be, that it can be simple or rather complicated.
Lynn
Maybe you are looking for
-
Download cd collection with itunes 12 2007 iMac?
Hello In the past, I have download my collection of entire cd in my imac 2007 without problem. I uptade my version of itunes at 12 and now, does not have my new cd I want to add. What can I do, please help, thanks,
-
Cannot drag files from the new iMac on my external hard drive that is already in use
I have a Seagate external hard drive that I used to back up files because my old iMac had difficulties. I bought a new iMac and can access the backup files, but cannot move the new files for the Seagate.
-
Want my iPhone and Apple Watch both ding when I get a text / SMS message.
My wife has a watch and iPhone 5 s and she wants SMS / text messages from the watch or the phone to beep. Is there a way to do this? If not, is there a way to make sure it's always the ringing telephone, even if the watch is connected?
-
Adding SSD to the second Bay drive in DV7-1285dx - advice please
So I recently bought a used DV7-1285dx and is considering the addition of a solid state drive to run the operating system. The current drive is 250 GB 5 400 rpm. Can I simply buy a 2.5 "SATA SSD to any size - I'm looking to 50 GB - and plop down insi
-
Password Wi - fi for iphone for printer
I have an office jet Pro 8600 Plus e all-in-one printer. When I go to WiFi on my iphone tells the printer it asks for a password.