Configuration of disk - size and speed?
According to the recommendations of the forum, I want to use raid0 on board for the swap file, media Cache because the rate of break-up for small media Cache files is best on the raid0. Because I need 2 with readers, how big and fast Gbps is usually sufficient?
Also, regarding recommended isolated disks for export (and cut projects I think)... should I go as fast and important that I can afford? Or more rather than faster depending on budget, so more room for storage?
C: [1 x 300 GB 10 K rpm Disk] OS, programs - CURRENT
[Raid0, 7200 2 discs] D: pagefile, hiding from media (edge) - NEED
E: [raid5, 4 x 1 t 7200 3 Gbit/s drives] previews of media, projects, (LSI/3Ware97504i) - COURSES
F: [1 player] exports, trimmed project - NEED
Thanks, NAN
Logical, but I would make sure that the export drive is the same make and model as those of your raid5.
RAID5 using only the built-in controller is very slow, so you can expand the raid 5 disks to increase his speed, and then you can use your drive to export this and get an external drive as export destination. First see if the speed edge it is good enough for your application, you decide to go on the road to raid extended or not.
Tags: Premiere
Similar Questions
-
Envy 17 t J000 - maximum hard drive size and speed
I'm going to put a 2nd hard drive into the open space in my Envy 17 t-j000.
The States of Maintenance and Service Guide;
Hard drives Supports 6.35 cm (2.5 in.) 9.5 mm hard disks (. 37-in) and thicknesses of 7.0 mm (. 28 - in) (all hard drives use the same bracket)
Customer-accessible
Serial ATA
Supports the following drives:
● 1 TB 5400 RPM, 9.5 mm
● 750 GB 5400 RPM 9.5 mm
● 500 GB 5400 RPM 9.5 mm and 7.0 mm
Configurations to two hard disks:
● 2 TB: (1 TB 5400 RPM x 2)
● 1500GO: (750 GB 5400 RPM x 2)
This seems to mean that I cannot use a single hard drive 2 TB 2 and cannot use a 7200 RPM drive.
Is this correct? Bios denominator do not allow more than a drive of 1 TB or the 7200 RPM?
CouldI partition just the 2nd 2-1 TB disk?
Or the manual simply means that the standard unit of HP is not provided with larger than these sizes and I could actually use a 2 TB in the Bay of 2nd?
It's the last... the list says just what HP sale: it does not describe a limitation of the system. However, I do not think that yet, the market offers a 2 TB drive that fits the available space. 2 TB 2.5-inch SATA drives I've seen are too thick. 7200 rpm or hybrid SSD; No problem.
To add a second drive you'll need a second hard drive enclosure and cable.
http://www.newmodeus.com/shop/index.php?Main_Page=product_info&cPath=2_5&products_id=542
If it's 'the Answer' please click on 'Accept as Solution' to help others find it.
-
Cloning a virtual machine to a disk size and model
Hi all, I cloned successfully a vm from a template. I resized the HDD in a new size of 50 GB 20 GB models and completed the conversion. The clone, the space allocated to the system partition remained 20 GB and shows the remaining new size (30 GB) size as unallocated space in disk management.
I called the Technical Support Center and they said that this is how it is supposed to be the case, although I previously resized the HDD when cloning and successfully using all the space reconfigured to the system partition. They recommended to convert the clone (using the converter) on another virtual computer and resize the disk. Anyone with a concrete solution to this is very welcome.
You are welcome.
Please consider awarding points by scoring responses like 'proper' or 'helpul.
-
Questions of size and speed of Collection stored
Hello everyone,
Developing a search engine for text, I was looking for a quick tool and low level storage. Berkeley DB I got and it seemed to suit my needs. I used Java cards to my process if it appeared logical to use the Collections API.
Structure database (or card):
DOCUMENT MAP
- docKey a simple integer ID generated in the order
- docEntry small number of properties
TERMMAP
- termKey, a unique string value
- termEntry small number of properties
INDEXMAP
- indexKey two foreign key values: docKey, termKey
-number of occurrence indexEntry of this term in the doc
There is a secondary index for INDEXMAP termKey interrogation.
I use the tuples of the key entities serializable for entries and I removed the redundant entities serializable key value using the transient modifier.
Here's the algorithm
The program retrieves the terms of a document and add the doc in the DOCUMENT Explorer.
For each term, if it is not in the TERMMAP, it is inserted.
This isn't in the INDEXMAP, it is inserted and the number of occurrence = 1 if the number of occurrence is triggered.
DOCUMENT map is quite small, while TERMMAP and INDEXMAP in particular have a huge amount of entries.
When testing it, it has very well worked and provided a quick mark. However, I noticed a few problems that could be critical:
-The size of the log is very high
1, 5 GB size of total newspaper for 100 MB of text indexing, then the same index (without the secondary index) takes 100 MB in ASCII text.
I tried to reduce the total log by increasing CLEANER_MIN_UTILIZATION but it has not reduced sufficiently.
I thought that maybe does not keep good things, but by displaying the contents of the card, all goes well, no redundancy.
-The storage is too slow
With a simple file storage, it's very fast if the bottleneck comes from db storage.
I noticed that it is faster to store temporary data in java cards (TreeMap to have sorted input values), then add them to the maps stored than to use the saved directly map.
To conclude
My final goal is to process a huge amount of data (collections of giga or terabyte) and I'll probably have to use parallel processing. However, if a simple test gives good results, I fear that I'll have to find another way to store my data.
This is the first time that I use berkeley db, so maybe I did something wrong. To avoid asking help for nothing I tried a lot of changes in the configuration: size, cleaner use, size of the cache, off transactional stuff and nothing gave significant results. I followed the tutorial for Java Collections and read the Javadoc. Finally, I used the JConsole plugin to take a look at the stats. This is my last chance...
If more details are needed, just ask,
Thank you in advance,
Nicolas.
-
Running out of disk space and the need to remove the old clichés
I recently joined a company owning an ESXi 4.1.0 (build 260247) server with 4 500GB data warehouses. One of our servers main database (Ubuntu/Postgres), which uses only one of the data warehouses (4 datastore) has 21GB 465 GB free. It is currently configured to store all settings, storage and snapshots on this unique data store. The hard disk is configured as thin.
The virtual machine has crashed a few days ago, when it ran out of disk space. We removed a small second partition (which was in the same data store) and cleared space, but we receive extremely weak with only 5% of the data left store.
I have read many posts and wanted to get the opinion of this community before I move forward. Because we do not use the 4.1 last I heard some issues using the option "Remove all" that it may require more disk space and others recommended to manually delete snapshots from the closest to the base, but it seems that in this case it can merge the snapshot with the original without freeing all the space.
We are not all of the snapshots and I'm fine with delete them, but I assure you we will not run out of disk space in the process and complicate things further.
It is best to manually remove these snapshots starting with the one closest to the base or by using the "Delete All" (or something else)? In addition, if we go with the manual option, is it possible with the virtual machine upward or do we need to close first?
Current snapshots:
Current data warehouses associated with VM (really unique using the 4 data store)
Actual files on the data store 4
Thank you
Brandon
Welcome to the community,
After the screenshot, your virtual disk 'arrow_db1.vmdk' stocked thickness!
With the thick disc service and ESXi 4.1 (the problem with "Delete All" is related to version 4.0), you can run safely "Delete All". However, due to low disk space, I recommend that do you with the virtual machine off. If turned on, a new temporary snapshot will be created, which - according to the workload of the virtual machine - can grow and fill in the data store.
Due to the size of snapshot and depending on the speed of your storage space, you need to plan a few hours well downtime.
André
-
I have windows xp home edition, he received from a friend. Tells me disk C and F are close to full. Make cleaning disc, but not enough. AND says the window is very low on storage space. Don't know what to delete and keep programs are
http://Windows.Microsoft.com/en-us/Windows-Vista/preventing-low-memory-problems
Read what you and answer a few questions about your system:
1. What is your current antivirus?
2.
Click Start, run and enter in the box:
Msinfo32
Click OK, and when the system info summary appears, click on edit, select all (Ctrl-A), copy (Ctrl-C) and paste (Ctrl-V) the information back here in your next reply.
You can change the personal information.
3. look in disk management, how many partitions? How much free space on each?
4. optimize your pc:
Stanley Zhang tips
Search for malware:
Download, install, execute, update and perform analyses complete system with the two following applications:
Remove anything they find. Reboot when necessary. (You can uninstall one or both when finished.)
Search online with eSet Online Scanner.
The less you have to run all the time, most things you want to run will perform:
Use Autoruns to understand this all starts when your computer's / when you log in. Look for whatever it is you do not know usingGoogle (or ask here.) You can hopefully figure out if there are things from when your computer does (or connect) you don't not need and then configure them (through their own built-in mechanisms is the preferred method) so they do not - start using your resources without reason.
You can download and use Process Explorer to see exactly what is taking your time processor/CPU and memory. This can help you to identify applications that you might want to consider alternatives for and get rid of all together.
Do a house cleaning and the dust of this hard drive:
You can free up disk space (will also help get rid of the things that you do not use) through the following steps:
Windows XP should take between 4.5 and 9 GB * with * an Office suite, editing Photo software, alternative Internet browser (s), various Internet plugins and a host of other things installed.
If you are comfortable with the stability of your system, you can delete the uninstall of patches which has installed Windows XP...
http://www3.TELUS.NET/dandemar/spack.htm
(Especially of interest here - #4)
(Variant: http://www.dougknox.com/xp/utils/xp_hotfix_backup.htm )You can run disk - integrated into Windows XP - cleanup to erase everything except your last restore point and yet more 'free '... files cleaning
How to use disk cleanup
http://support.Microsoft.com/kb/310312You can disable hibernation if it is enabled and you do not...
When you Hibernate your computer, Windows saves the contents of the system memory in the hiberfil.sys file. As a result, the size of the hiberfil.sys file will always be equal to the amount of physical memory in your system. If you don't use the Hibernate feature and want to reclaim the space used by Windows for the hiberfil.sys file, perform the following steps:
-Start the Control Panel Power Options applet (go to start, settings, Control Panel, and then click Power Options).
-Select the Hibernate tab, uncheck "Activate the hibernation", and then click OK. Although you might think otherwise, selecting never under "Hibernate" option on the power management tab does not delete the hiberfil.sys file.
-Windows remove the "Hibernate" option on the power management tab and delete the hiberfil.sys file.You can control the amount of space your system restore can use...
1. Click Start, right click my computer and then click Properties.
2. click on the System Restore tab.
3. highlight one of your readers (or C: If you only) and click on the button "settings".
4 change the percentage of disk space you want to allow... I suggest moving the slider until you have about 1 GB (1024 MB or close to that...)
5. click on OK. Then click OK again.You can control the amount of space used may or may not temporary Internet files...
Empty the temporary Internet files and reduce the size, that it stores a size between 64 MB and 128 MB...
-Open a copy of Microsoft Internet Explorer.
-Select TOOLS - Internet Options.
-On the general tab in the section 'Temporary Internet files', follow these steps:
-Click on 'Delete the Cookies' (click OK)
-Click on "Settings" and change the "amount of disk space to use: ' something between 64 MB and 128 MB. (There may be many more now.)
-Click OK.
-Click on 'Delete files', then select "Delete all offline content" (the box), and then click OK. (If you had a LOT, it can take 2 to 10 minutes or more).
-Once it's done, click OK, close Internet Explorer, open Internet Explorer.You can use an application that scans your system for the log files and temporary files and use it to get rid of those who:
CCleaner (free!)
http://www.CCleaner.com/
(just disk cleanup - do not play with the part of the registry for the moment)Other ways to free up space...
SequoiaView
http://www.win.Tue.nl/SequoiaView/JDiskReport
http://www.jgoodies.com/freeware/JDiskReport/index.htmlThose who can help you discover visually where all space is used. Then, you can determine what to do.
After that - you want to check any physical errors and fix everything for efficient access"
CHKDSK
How to scan your disks for errors* will take time and a reboot.Defragment
How to defragment your hard drives* will take timeCleaning the components of update on your Windows XP computer
While probably not 100% necessary-, it is probably a good idea at this time to ensure that you continue to get the updates you need. This will help you ensure that your system update is ready to do it for you.
Download and run the MSRT tool manually:
http://www.Microsoft.com/security/malwareremove/default.mspx
(Ignore the details and download the tool to download and save to your desktop, run it.)Reset.
Download/install the latest program Windows installation (for your operating system):
(Windows XP 32-bit: WindowsXP-KB942288-v3 - x 86 .exe )
(Download and save it to your desktop, run it.)Reset.
and...
Download the latest version of Windows Update (x 86) agent here:
http://go.Microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=91237
... and save it to the root of your C:\ drive. After you register on theroot of the C:\ drive, follow these steps:Close all Internet Explorer Windows and other applications.
AutoScan--> RUN and type:
%SystemDrive%\windowsupdateagent30-x86.exe /WUFORCE
--> Click OK.(If asked, select 'Run'). --> Click on NEXT--> select 'I agree' and click NEXT--> where he completed the installation, click "Finish"...
Reset.
Now reset your Windows with this FixIt components update (you * NOT * use the aggressive version):
How to reset the Windows Update components?Reset.
Now that your system is generally free of malicious software (assuming you have an AntiVirus application), you've cleaned the "additional applications" that could be running and picking up your precious memory and the processor, you have authorized out of valuable and makes disk space as there are no problems with the drive itself and your Windows Update components are updates and should work fine - it is only only one other thing youpouvez wish to make:
Get and install the hardware device last drivers for your system hardware/system manufacturers support and/or download web site.
-
Should we leave how much free space on the C drive before affecting the performance and speed?
Hello!
Hard drive of my new PC (C) is 1 TB (processor Samsung 7i, Windows 8.1). It doesn't have any other disk/partition. How this space is safe to use to store large files (videos, esp., stored in the native video library file) without harming the performance and speed?
And if I create another partition (D) and just use it for storage, it will make much difference compared to the above?
Thank you!
Anna
Sunday, March 1, 2015 10:59 + 0000, AnaFilipaLopes wrote:
And if I create another partition (D) and just use it for storage, it will make much difference compared to the above?
Planning your Partitions
The Question
Partitions, how much should I have on my hard drive, what do I use
each of them for, and what size should each one be?It s a common question, but unfortunately this doesn t have a
only simple, just answer to all the world. A lot of people will respond with
the way they do, but their response isn't necessarily best for the
person seeking (in many cases it isn't right even for the person)
response).Terminology
First, let's rethinking the terminology. Some people ask "should I".
partition my drive? That s the wrong question, because the
the terminology is a little strange. Some people think that the word
"partition" means divide the drive into two or more partitions.
That s not correct: to partition a drive is to create one or several
partitions on it. You must have at least one partition to use
He who think they have an unpartitioned disk actually
have a player with only one partition on it and it s normally
Called C:. The choice you have is to have more than one
partition, not that it's the partition at all.A bit of history
Back before Windows 95 OEM Service Release 2 (also known as Windows
95 (b) was published in 1996, all MS-DOS and Windows hard drives have been set
using the file system FAT16 (except for very tiny to aid
FAT12). That 16-bit only because were used for addressing, FAT16 has a
maximum 2 GB partition size.More than 2 GB of hard disks were rare at the time, but if you had
one, you must have multiple partitions to use all the available
space. But even if your drive was not larger than 2GB, FAT16 created
Another serious problem for many people - the size of the cluster has been
more great if you had a larger partition. Cluster sizes increased from 512
bytes for a partition to no greater than32Mb all the way up to 32 KB for a
partition of 1 GB or more.More the cluster size, the space more is wasted on a hard drive.
That s as space for all the files is allocated in whole clusters
only. If you have 32 KB clusters, a 1 byte file takes 32 KB, a file, a
greater than 32 k byte takes 64 k and so on. On average, each file
about half of his last group waste.If large partitions create a lot of waste (called "soft"). With a 2 GB
FAT16 drive in a single cluster, if you have 10,000 files, each
lose half a cluster of 32 KB, you lose about 160 MB for relationships. This s
back in an important part of a player that probably cost more than $400
1996 - around $ 32.So what did the people? They divided their 2 GB drive in two,
three or more logical drives. Each of these logical drives has been
smaller the real physical disk, had smaller clusters, and
so less waste. If, for example, she was able to keep all the partitions
less than 512 MB, cluster size was only 8 KB, and the loss was reduced to a
a quarter of what it would be otherwise.People partitioned for other reasons also, but back in the days of
FAT16, it was the main reason to do so.The present
Three things have changed radically since 1996:
1. the FAT32 and NTFS file systems came along, allowing a larger
partitions with smaller clusters and so much less waste. In
with NTFS, cluster sizes are 4 K, regardless of the size of the partition.2 hard drives have become much larger, often more than 1 TB (1000 GB) in
size.3 hard drives have become much cheaper. For example, a 500 GB drive
can be bought today for about $50. That s 250 times the size of this
Player 2Gb typical 1996, about one-eighth of the price.What these things mean together which is the reason to be old to have
multiple partitions to avoid the considerable wastage of disk space left.
The amount of waste is much less than it used to be and the cost of
that waste is much less. For all practical purposes, almost nobody does
should no longer be concerned about slack, and it should no longer be
has examined when planning your partition structure.What Partitions are used for today
There are a variety of different ways people put in place several
scores of these days. Some of these uses are reasonable, some are
debatable, some are downright bad. I'll discuss a number of Commons
partition types in the following:1. a partition for Windows only
Most of the people who create such a partition are because they believe
If they never have to reinstall Windows properly, at least they
He won t lose their data and he won t have to reinstall their applications.
because both are safe on other partitions.The first of these thoughts is a false comfort and the second
is downright bad. See the analysis of the types of partition 2 and 4
below to find out why.Also note that over the years, a lot of people who find their windows
partition that has begun to be the right size proves to be too
small. For example, if you have such a partition for Windows and later
upgrade to a newer version of Windows, you may find that your Windows
partition is too small.2. a partition for installed programs
This normally goes hand in hand with the partition type 1, a partition for
just Windows. The thought that if you reinstall Windows, your
installed application programs are safe if they are in another
partitions is simply not true. That s because all programs installed
(with the exception of an occasional trivial) have pointers to the inside
Windows, in the registry and elsewhere, as well as associated files
buried in the Windows folder. So if Windows, pointers and
the files go with it. Given that the programs need to be reinstalled if Windows
the fact, this reasoning to a separate partition for programs not
work. In fact, there is almost never a good reason to separate
Windows of the software application into separate partitions.3. a partition for the pagefile.
Some people think mistakenly that the pagefile on another
score will improve performance. It is also false; It doesn t
help and often I hurt, performance, because it increases the movement of the head
to get back to the page to another file frequently used
data on the disk. For best performance, the paging file should normally
be on the most widely used score of less used physical player. For
almost everyone with a single physical disk than the same drive s
Windows is on C:.4. a partition for backup for other partitions.
Some people make a separate partition to store backups of their other
or partitions. People who rely on a "backup" are a joke
themselves. It is only very slightly better than no backup at all.
because it leaves you likely to be simultaneously the original losses
and backup for many of the most common dangers: the head crashes and other
types of drive, serious glitches to power failure, near lightning
strikes, virus attack, even stolen computer. In my opinion,.
secure backup must be on a media removable and not stored in the
computer.5. a partition for data files
Above, when I discussed separate Windows on a clean partition,
I pointed out that separate data from Windows is a false comfort if
He of done with the idea that data will be safe if Windows ever
must be reinstalled. I call it a false comfort that's because
I'm afraid many people will rely on this separation, think that their
data are safe there and so do not take measures to
Back it up. In truth the data is not safe there. Having to reinstall
Windows is just one of the dangers to someone a s hard disk and not
probably even one. This kind of "backup" falls into the same
category, as a backup to other partitions partition; It lets you
sensitive to the simultaneous loss of the original and the backup on many of
the most common dangers that affect the entire physical disk, not
just the particular partition. Security comes from a solid backup
diet, not how partition you.However, for some people, it may be a good idea to separate Windows and
programs on the one hand of the data on the other, putting each of the
two types into separate partitions. I think that most people
partitioning scheme must be based on their backup system and backup
plans are generally of two types: whole hard disk imaging
or data only backup. If you back up data, backup is
usually facilitated by the presence of a separate with data only partition;
to save just the score easily, without having to
collect pieces from here and elsewhere. However, for
those who backup by creating an image of the entire disk, there is
usually little, if any, benefit the separation of data in a partition of
its own.Furthermore, in all honesty, I must point out that there are many
very respected people who recommend a separate partition for Windows,
Whatever your backup plan. Their arguments haven t convinced
me, but there are clearly two views different here.6. a partition to image files
Some people like to deal with the images and videos as something separate
other data files and create a separate partition for them. To my
the spirit, an image is simply another type of data and there is no
the advantage in doing so.7. a partition for music files.
The comments above related to the image files also apply to music
files. They are just another type of data and must be dealt with the
just like the other data.8. a partition for a second operating system to dual-boot to.
For those who manage several operating systems (Windows Vista, Windows
XP, Windows 98, Linux, etc.), a separate partition for each operating
system is essential. The problems here are beyond the scope of this
discussion, but simply to note that I have no objection to s
all these partitionsPerformance
Some people have several partitions because they believe that it
somehow improves performance. That s not correct. The effect is
probably low on modern computers with modern hard disks, but if
whatever it is, the opposite is true: more music mean poorer
performance. That's because normally no partition is full and it
so are gaps between them. It takes time for the drive s
read/write heads to cross these gaps. Close all files
are, faster access to them will be.Organization
I think a lot of people overpartition because they use scores as a
organizational structure. They have a keen sense of order and you want to
to separate the apples from the oranges on their readers.Yes, separating the different types of files on partitions is a
technical organization, but then is to separate different types of
files in folders. The difference is that the walls are static and
fixed in size, while the files are dynamic, changing size automatically
as needed to meet your changing needs. This usually done records
a much better way to organize, in my opinion.Certainly, partitions can be resized when necessary, but except with the latter
versions of Windows, which requires a third-party software (the and the
possibility to do so in Windows is primitive compared to the third-party
solutions). These third party software normally costs money and not
any point and how stable it is, affects the entire disk.
with the risk of losing everything. Plan your partitions in
first place and repartitioning, none will be necessary. The need
to repartition usually occurs as a result of overpartitioning in
the first place.What often happens when people organize with partitions instead
records are that they make a miscalculation of how much room they need on each
This partition, and then when they run out of space on the partition
When a file is logically, while having plenty of space
on the other hand, they simply saving the file in the score of "poor".
Paradoxically, therefore, results in this kind of score structure
less organization rather than more.So how should I partition my drive
If you read what came before, my findings will not come as a
surprise:1. If your backup set is the image of the entire disk, have just one
single (usually c partition :));2. If you backups just data, have two partitions one for Windows and
application programs installed (usually c :)), the other for data
(normally D :).)With the exception of multiple operating systems, it is rarely
any advantage to have more than two partitions. -
disk size problm after copying a large file to the VM then disconnected
Dear Sir
I have a VM with allowances dynamic storage virtual hard drive of 300 GB,.
HE on that disk space is 50 GB.
Ive copied on it a 100 GB file so now space space disc is 150 GB and 150 GB is free.
Ive deleted the file 100 GB of the virtual machine, but am supersized now that the file of the virtual machine is still 150 GB in size.
What should do? as it fits the 50 GB after deleting the file from the virtual machine.
Hello
Yes it is planned.
You have copied a huge file in the virtual computer-> who is the virtual disk in order to accommodate the new file->
You remove the huge file-> your take off just to comments operating system, the file in the list of the directory->
Your data is still there, it does not erase the data and rewrite from scratch.
In order to recover the disk space, you need a number of things:
-first of all your guests, OS file system must be supported (Windows FAT/NTFS is)
-Your guest must be stopped
-The type of the guest operating system disk should not be preallocated.
-Your host operating system might need a lot of free space on the drive according to your VM disk configuration.
If stored in several files, you must have a few GB free (size of the Ramdisk / 32) Go, but say more than 4 GB, keep 10 GB free to be on the safe side.
If your virtual machine is stored in a single file, so you must have your used VM disk size + a few GB of free... for example. If your virtual disk is currently using 200 GB you need tell 204 GB free before starting the operation of a compact disc.
Then in the configuration of VMware go into settings of virtual machines:
Use the 'Compact disc' button.
Be very very patient and wait, because you want to get 100GB which will take some time.
--
Wil
-
vSphere on iSCSI SAN disk size
Hello
I installed the 5.1 version and will also use VMWare View.
I see in the documentation that there always a size of 2 TB drive but also given conflicting reports on that. I tested it and I see that he can see more then 2 TB.
My question is if I want to 2 TB standard or can we go more then 2 TB and if yes, what size Max now.
Thank you.
GaryHello
If you're talking about VMFS datastore now we support 64 to http://www.vmware.com/pdf/vsphere5/r50/vsphere-50-configuration-maximums.pdf
If you talk about virtual disk, virtual disk size 2 TB less 512 bytes
Concerning
Mohammed
-
disk memory and space requirment for development database
Hi all
I want to know the disk space and memory required for the configuration of the environment development database.
Production database size is max 25 to 30 concerts
and only 3 user will use this database
on this info my suggesion is to go with 3 GB memory 60 GB of backup space and archivelog. Let me know experts comment on thatxuv500 wrote:
I want to know the disk space and memory required for the configuration of the environment development database.
Production database size is max 25 to 30 concerts
and only 3 user will use this databaseon this info my suggesion is to go with 3 GB memory 60 GB of backup space and archivelog. Let me know experts comment on that
How long lasts this string? +
+ So, in other words - it depends. Development environment might include a database logic dev (containing data from prod), one database Q & A logic (to test changes in dev) and a complete copy of the prod database logic (to test the final deployment).
It could contain an R & D environment - where all data from prod is necessary for data mining research and then to deploy processes of extraction of useful data in the production.
It could be used in a number of ways - and some of them will be more intensive in the transformation and requiring more data, than the production.
Ideally - dev environment should look like as close as possible to the prod environment. Ideally, that means a server hardware and similar size, same o/s and Oracle versions and same volumes of data.
-
The distribution of applications and data between the disk SSD and HDD
I recently installed an SSD in my Macbook Pro (late 2011) instead of the DVD player. I want to install OS X on it, by replacing the current OS X on the original hard disk, I will continue to use for storing files. How should I allocate its use in car? OS X and applications on the data files on the hard disk of 500 GB and SSD?
The first series of instructions will partition and format the newly installed SSD disk then install OS X on it. The second block will help you configure OS X on the SSD with your data on the HARD drive.
Clean Install of El Capitan on a new disc
- Restart the computer. Immediately after the chime, press Command + Option + R until a globe appears.
- The Utility Menu appears in 5 to 20 minutes. Be patient.
- Select disk utility, then click on the continue button.
- When loading disk utility, select the drive (generally, the entry Out-bumpy) in the list aside.
- Click the Partition tab in the main window of disk utility. A panel will fall.
- Set the GUID partition scheme.
- Define the type of Format Mac OS extended (journaled).
- Click on the apply button, then click the fact when it is active.
- Quit disk utility and re-enter the Utility Menu.
- Select reinstall OS X and click on the continue button.
How to use an SSD with your HARD drive
If you want to use an SSD as boot with your existing HARD disk drive, as the disk 'data', here is what you can do.
After installing the SSD, you need to partition and format the SSD using disc utility disc. Then install OS X on the SSD. Once installed OSX boot from SSD. Startup disk preferences to set up the SSD as the boot volume.
Open the preferences users and groups. Click the lock and authenticate you. Or CTRL - RIGHT click on your username account list in the sidebar and select Advanced Options in the context menu. You will see a field called "Home dir: ' on the far right, you will see an Edit button. Click on it. In the file dialog box, navigate to the location in house now located on the HARD disk (disk HARD/users/user_name /.) Select the folder, click the Open button. Restart the computer, as shown. When the computer starts, it will now use the home located on the HARD drive folder.
Another more technical method involving the Terminal and the alias is discussed in depth here: using OS X with a SSD and HDD - Matt Gemmell configuration. It's my preferred approach because I can choose which records of the House, I want to on the HARD drive and I don't want to. For example, I like to keep Documents and library files on the SSD because I frequently access their content.
Make sure that you keep the bootable system entirely on your HARD drive where you need it.
-
SSDS must be similar in size and type to raid 0?
SSDS must be similar in size and type to raid 0? I have a 2009 MBP 2.66 bicoeur. SSDS are an old sata 250 GB Samsung 850 pro III and an all new Intel 160 GB (320 series) sata II. The hard drive on the MBP interface is 3.0 GB/s sata optical drive interface is 3.0 Gbit/s
Different size, different brand, sata II issue III v?
If it works, it will be almost double the read and write rates, I understand. I am aware of the increased risk of data loss. Will only use for backup data.
How is it difficult to set up raid 0? I don't know the first thing about raid 0, 1, 2, 3?
Thank you
Stu
If it works, it will be almost double the read and write rates, I understand.
RAID offers for the SECOND and the following read/write of the same LARGE file acceleration and not otherwise. Any intervention of reading or writing in different files eliminates the acceleration. Any acceleration is much more dramatic on rotating discs, because it can eliminate some of the 10 ms or more long 'dead time' while the reader is a new track and the controller must wait for the correct data go in the position under the read/write head. Acceleration on the low-latency SSDS is far less dramatic.
The system drive / boot is particularly bad choice for a RAID, it reads and writes small random files in all directions. Who will get no acceleration.
You can best be served by creating a workflow that allows separate readers for the source files to Destination files, files of zero and drive system / boot.
--------
RAID is usually done on the disks that are exactly or nearly the same. Too slow response of one of the discs can cause the RAID failure.
RAID support has been removed the disc utility GUI in 10.11 ElCapitan, probably because too many casual users got into trouble with the built-in GUI functions. You need to use the diskutil command in the Terminal, or buy the SoftRAID(4) package.
-
I want to replace the original 80 MB HARD drive of my Z61m by a faster and bigger. What't maximum disk size THE controller BIOS / able to face?
Gurk
Any laptop SATA drive will do just fine, whether it's 160 GB or 320 GB. You know your needs and your budget best.
I hope this helps.
-
buffer size and sync with the cDAQ 9188 problems and Visual Basic
Hi all, I have a cDAQ-9188 with 9235 for quarter bridge straing caliber acquisition module.
I would appreciate help to understand how synchronization and buffer.
I do not use LabView: I'm developing in Visual Basic, Visual Studio 2010.
I developed my app of the NI AcqStrainSample example. What I found in the order is:
-CreateStrainGageChannel
-ConfigureSampleClock
-create an AnalogMultiChannelReader
and
-Start the task
There is a timer in the VB application, once the task begun, that triggers the playback feature. This function uses:
-AnalogMultiChannelReader.ReadWaveform (- 1).
I have no problem with CreateStrainGageChannel, I put 8 channels and other settings.
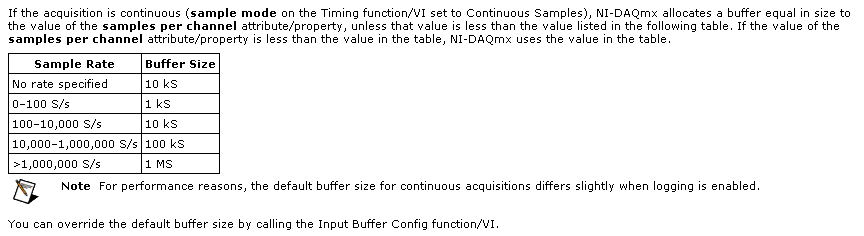
Regarding the ConfigureSampleClock, I have some doubts. I want a continuous acquisition, then I put the internal rate, signal source 1000, continuous sample mode, I set the size buffer using the parameter "sampled by channel.
What I wonder is:
(1) can I put any kind of buffer size? That the limited hardware of the module (9235) or DAQ (9188)?
(2) can I read the buffer, let's say, once per second and read all samples stored in it?
(3) do I have to implement my own buffer for playback of data acquisition, or it is not necessary?
(4) because I don't want to lose packets: y at - it a timestamp index or a package, I can use to check for this?
Thank you very much for the help
Hi Roberto-
I will address each of your questions:
(1) can I put any kind of buffer size? That the limited hardware of the module (9235) or DAQ (9188)?
The samplesPerChannel parameter has different features according to the synchronization mode, you choose. If you choose finished samples the parameter samplesPerChannel determines how many sample clocks to generate and also determines the exact size to use. But if you use streaming samples, the samplesPerChannel and speed settings are used together to determine the size of the buffer, according to this excerpt from the reference help C DAQmx:
Note that this buffer is a buffer software host-side. There can be no impact on the material available on the cDAQ-9188 or NI 9235 buffers. These devices each have relatively small equipment pads and their firmware and the Driver NOR-DAQmx driver software transfer data device to automatically host and the most effective way possible. The buffer on the host side then holds the data until you call DAQmx Read or otherwise the input stream of service.
(2) can I read the buffer, let's say, once per second and read all samples stored in it?
Yes. You would achieve this by choosing a DAQmx Read size equal to the inverse of the sampling frequency (during 1 second data) or a multiple of that of the other playback times.
(3) do I have to implement my own buffer for playback of data acquisition, or it is not necessary?
No, you should not need to implement your own stamp. The DAQmx buffer on the host side will contain the data until you call the DAQmx Read function. If you want to read from this buffer less frequently you should consider increasing its size to avoid the overflow of this buffer. Which brings me to your next question...
(4) because I don't want to lose packets: y at - it a timestamp index or a package, I can use to check for this?
DAQmx will meet you if all packets are lost. The default behavior is to stop the flow of data and present an error if the buffer of the side host DAQmx overflows (if, for example, your application does not pick up samples of this buffer at a rate equal or faster than they are acquired, on average).
If, for any reason, you want to let DAQmx to ignore the conditions of saturation (perhaps, for example, if you want to sample continuously at a high rate but want only interested in retrieving the most recent subset of samples), you can use the DAQmxSetReadOverWrite property and set it to DAQmx_Val_OverwriteUnreadSamps.
I hope this helps.
-
Envy touchsmart 15 - new HARD disk size
I recently ordered a Touchsmart from HP Envy 15-j005sa that has a 1 TB HARD drive. I'm looking to clone the orignial in an mSATA SSD drive so I was wondering what size is recommended. How much space is used when it is new so using this information can buy a large enough disk size?
Thanks in advance
Hello
There is that little clone options b clone the HARD disk which means that you have the mSATA SSD equal or more 1 TB (b) clone c ONLY: This means you the mSATA SSD equal or superior to c:... My suggestion: shrink C: for small size say even 60 GB or 120 GB (if you don't have a lot of programs installed) FRONT of clone and ONLY clone C: normally larger (capacity) is better because you can install more programs that him.
Kind regards.
Maybe you are looking for
-
How Long it take for the recovery disk to install?
I have the original recovery disc for my Toshiba M55-S139 laptop. I've never used up yeserday. Well its been 17 hrs and nothing! Is this normal? When I put the cd in, it seems, to copy files, etc., so he asks that I remove the disk and press any key
-
original title: java Sorry, I should add that to my saved question the offline download when I went to install it says already installed u would like to reinstall it click Yes, and then box comes up the oonly valid action for the currently installed
-
How to import and transport of the images in the flash player
How to export images to my Windows live photo gallery flash drive. I know how to import but not export it from my computer.
-
How to open files .icl with windows 7? Windows used to open the...
Windows used to use and open with ease .icl files, now the links are fake registry cleaner links, not interested in sites of unrest.
-
Retrieve data from a data Bitlocker Drive lost like BRUT space
original title: MBR error? BitLocker data reader lost as RAW space... help get it back me? (Please...) OK I was experimenting with a system dual boot and naively assumes that it would protect my system Windows 7 of all the problems to have 2 separate